Conflicts
Politics
“ HAY ’, ABU MOHAMMAD AL - JOLANI, AL, ASIA, ASSAD, CNN, CONFLICT, EUROPE, EUROPE/ASIA, H. T, H. T. S, HAMA, ISIS, MIDDLE EAST, MILITARY, MILITARY OPERATIONS, NEW YORK TIMES, R. F. I, REUTERS, RUSSIA, SYRIA, SYRIAN CIVIL WAR, SYRIAN CONFLICT, THE NEW YORK TIMES, TURK, WAR
Dante Raeburn
The Withered Rose of Damascus: Reigniting Syria’s Civil War
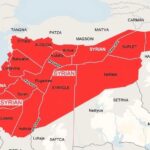
Syria’s second civil war has reignited, with armed opposition led by Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (H.T.S.) capturing critical cities, including Hama and Homs. This resurgence of conflict has led to the displacement of over 280,000 people and poses significant humanitarian challenges. The complexities of sectarian divisions, external support from Sunni Arab nations to opposition forces, and ongoing geopolitical struggles involving the U.S. and Russia underscore a fraught landscape for Syria and the broader region.
The situation in Syria is deteriorating once again, as armed opposition forces have advanced into critical cities, including Hama and Homs, amidst what is being termed Syria’s second civil war. The military group Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (H.T.S.) has emerged as a significant rebel faction, proclaiming their intention to overthrow the Al-Assad regime. This military engagement highlights the fragmentation of Syrian society along sectarian and political lines, as multiple factions are unexpectedly uniting against a common adversary.
The historical turmoil in Syria can be traced back to a variety of factors, including internal strife between sects, particularly the ruling Alawite minority and the Sunni majority. Regional dynamics add to the complexity; Sunni states, notably Turkey and Saudi Arabia, are accused of providing support to opposition forces while countering Shiite influence from Iran. The United States, meanwhile, is deeply involved in supporting Kurdish factions, illustrating how the Syrian conflict has become a proxy battleground for major global powers.
As the civil war resumes, reports indicate that over 280,000 people have been displaced since late November 2024, underscoring the severe humanitarian crisis unfolding as the conflict escalates. Coupled with diplomatic mediation efforts, there exists a troubling reality: a lack of genuine intentions for democratic stability among various factions.
The outcome of this renewed conflict is uncertain. As the H.T.S. rises in power, the international community must consider whether it is fostering a regime capable of bringing reform or a continuation of terror. The volatility of the region, the potential for further displacement of millions, and the wider geopolitical implications necessitate urgent humanitarian responses and a reevaluation of foreign involvement in Syria’s ongoing crisis.
The recent advancements by opposition forces in Syria signal a grim continuation of the nation’s civil war, characterized by deeply rooted sectarian divisions and an increasingly complex international engagement. Historically, Syria has faced significant instability due to various internal and external pressures, including political fragmentation and competing interests from foreign powers attempting to sway the balance of influence. Negotiations for peace have persistently failed, leading to a painful stalemate since 2020, which abruptly terminated with the recent escalations. The Al-Assad regime has not only contended with internal opposition but also with aggressive foreign interventions that complicate any hopes for a unified resolution. With factions coalescing against the regime and external support exacerbating the conflict, the humanitarian implications are dire, and international support is becoming increasingly critical.
In conclusion, the resurgence of violence in Syria marks a significant and concerning development in the Middle East. The confluence of internal divisions, sectarian conflicts, and the involvement of major international players complicates the landscape. The humanitarian crisis necessitates immediate support from the international community while the geopolitical consequences remain to be fully realized. Ultimately, the future of Syria hinges on the actions of its people and the overarching influences of regional and global powers.
Original Source: theowp.org







Post Comment